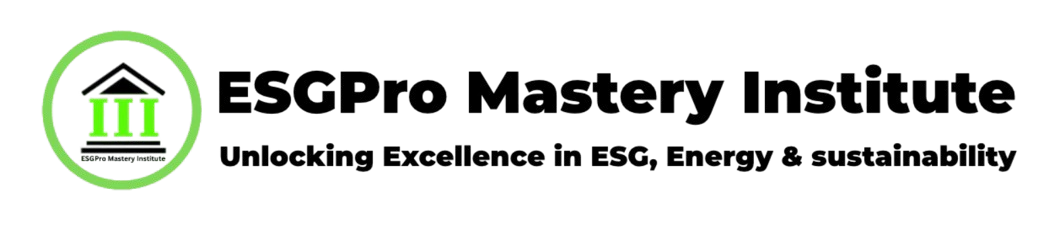The financial world is undergoing a significant transformation, with ESG investing at its forefront, rapidly reshaping the landscape of sustainable finance. This approach, focusing on Environmental, Social, and Governance factors, is no longer a niche concept but a mainstream imperative for investors and businesses alike. Understanding why ESG investing trends are gaining such momentum is crucial for anyone involved in finance or interested in creating a more sustainable future. This article delves into the reasons behind this surge, exploring its impact, benefits, and future trajectory within the sustainable finance growth paradigm.
Q&A: Unpacking the ESG Investing Phenomenon
This section addresses key questions to provide a comprehensive understanding of why ESG investing is becoming increasingly important in sustainable finance.
Q: What exactly is ESG investing, and how does it differ from traditional investment approaches?
A: ESG investing, also known as sustainable investing, responsible investing, or impact investing, considers environmental, social, and governance factors alongside financial metrics when making investment decisions.
- Environmental criteria include a company’s impact on climate change, pollution, waste management, and resource conservation. For instance, examining if an issuer protects and/ or conserves natural resources.
- Social criteria assess a company’s relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities in which it operates, encompassing aspects like human rights, labor standards, and diversity and inclusion. For example, looking at how an issuer manages its relationships with individuals, such as its employees, shareholders, and customers as well as its community.
- Governance criteria examine a company’s leadership, executive compensation, shareholder rights, and ethical business practices.
Unlike traditional investing, which primarily focuses on maximizing financial returns, ESG investing seeks to generate positive societal and environmental outcomes in addition to financial gains.
Q: What are the primary drivers behind the increasing popularity of ESG investing trends?
A: Several factors contribute to the rise of ESG investing trends:
- Growing awareness of environmental and social issues: Increased public awareness of climate change, social inequality, and corporate misconduct has fueled demand for investments that align with ethical values. For example, consider the increasing consumer demand for products from companies with strong sustainability track records.
- Regulatory pressures: Governments worldwide are implementing regulations that require companies to disclose ESG-related information, promoting transparency and accountability. Nadia Kalic, a Partner in the Corporate M&A Group, says: “Over the last few years we have witnessed an uptick in sustainability-related reporting and disclosure obligations globally.”
- Investor demand: Both institutional and retail investors are increasingly seeking ESG-aligned investment options, driven by a desire to make a positive impact and mitigate risks associated with unsustainable business practices. This is especially true among Millennials, with over 40 percent engaging in impact investing, compared to only 20 percent of Baby Boomers.
- Improved financial performance: Studies suggest that ESG-integrated investments can perform as well as or even better than traditional investments, dispelling the myth that ethical investing comes at the expense of financial returns. An Institute analysis of Morningstar data shows that investing a hypothetical $100 into a sustainable fund in December 2018 would equate to $154 today, while investing $100 into a traditional fund over the same period would equate to $145 today.
- Technological advancements: Rising interest in AI and data analytics (65%) to better understand ESG factors. This is evident from the sector seeing rising interest in AI and data analytics (65%), impact investing (58%), and the diversification of ESG-focused asset.
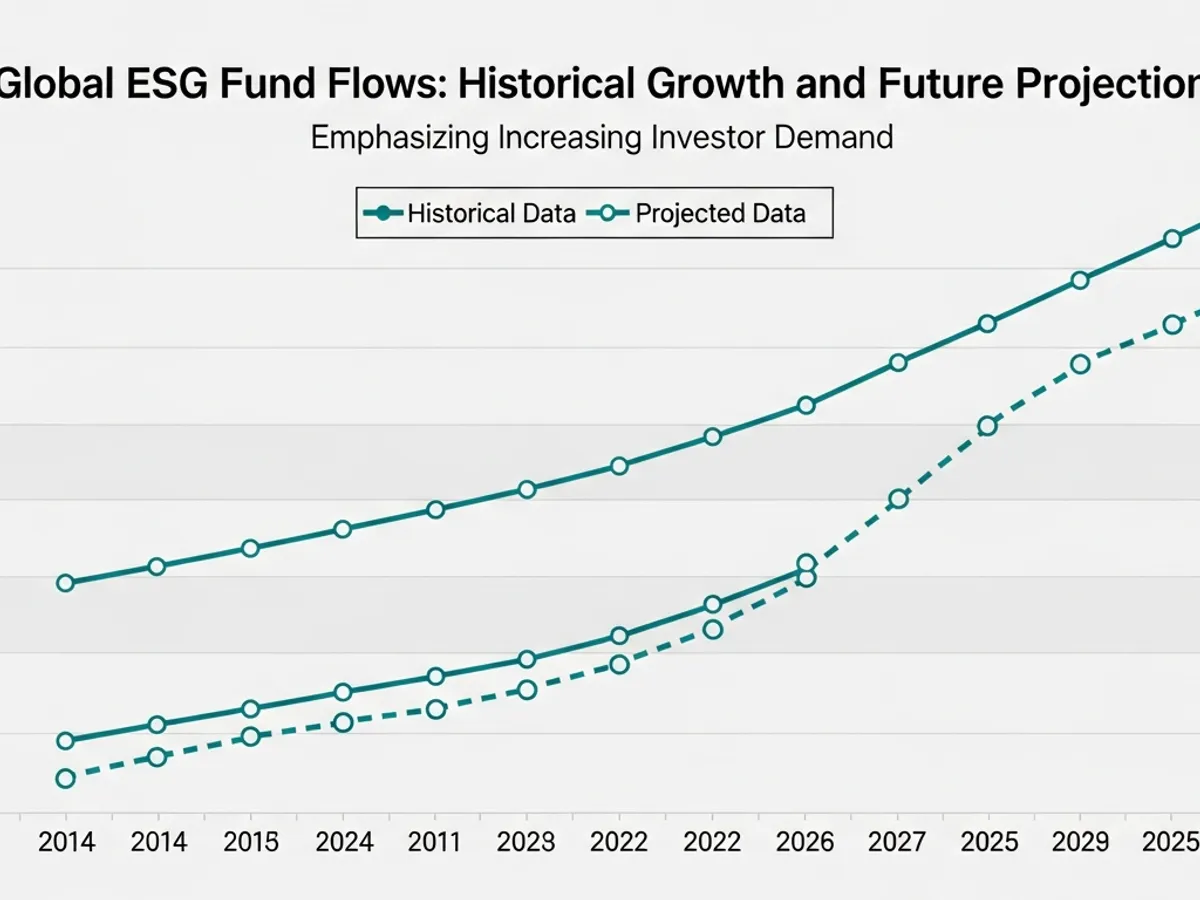
Q: How has the growth of sustainable finance contributed to the rise of ESG investing?
A: The sustainable finance growth has been a key catalyst for the widespread adoption of ESG investing. Sustainable finance impact, which encompasses various financial instruments and strategies aimed at promoting environmental and social sustainability, provides a framework for channeling capital towards ESG-aligned investments.
- Green bonds, for example, are used to finance environmentally friendly projects such as renewable energy and energy efficiency initiatives.
- Social bonds support projects with positive social outcomes, such as affordable housing and healthcare.
- Sustainability-linked loans incentivize companies to achieve specific ESG targets by offering lower interest rates.
The growth of these sustainable finance instruments has created a broader ecosystem for ESG investing, making it easier for investors to allocate capital to companies and projects that prioritize sustainability. The sustainable finance market grew to more than $8.2 trillion in 2024, up 17 per cent from 2023, but faced intensified headwinds and.
Q: What are the key benefits of impact investing benefits, and how can investors measure them effectively?
A: Impact investing aims to generate specific social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns. The impact investing benefits can be significant, including:
- Addressing pressing global challenges: Impact investments can help tackle issues such as poverty, climate change, and access to healthcare and education. For instance, investments in renewable energy projects directly combat climate change.
- Driving innovation: By supporting companies and projects with a social or environmental mission, impact investing can foster innovation and create new solutions to global problems. Supporting companies that limit water consumption or carbon emissions.
- Enhancing brand reputation: Companies that prioritize social and environmental impact can attract customers, employees, and investors who value sustainability.
Measuring the impact of ESG investments can be challenging, but several frameworks and methodologies are available to help investors assess their social and environmental performance effectively:
- Impact Reporting and Investment Standards (IRIS): Provides a common set of metrics for measuring social and environmental impact.
- Global Impact Investing Network (GIIN): Offers resources and tools for impact investors, including a database of impact investments and a framework for measuring impact.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): Develops industry-specific standards for reporting on ESG issues.
Q: How are ESG funds and ESG ETFs reshaping the investment landscape?
A: ESG funds and ESG ETFs are becoming increasingly popular as they offer investors a convenient and diversified way to incorporate ESG principles into their portfolios.
- ESG funds are mutual funds that invest in companies with strong ESG performance.
- ESG ETFs are exchange-traded funds that track ESG indices, providing diversified exposure to ESG-rated companies. Like mutual funds, ETFs provide diversified exposure to ESG-rated companies but with the added flexibility of trading on stock exchanges like individual stocks.
These funds offer several advantages:
- Diversification: ESG funds and ETFs provide exposure to a broad range of companies across different sectors, reducing investment risk.
- Accessibility: ESG funds and ETFs are readily available to both retail and institutional investors, making it easier to invest in ESG-aligned companies.
- Transparency: ESG funds and ETFs typically disclose their ESG criteria and holdings, allowing investors to understand how their investments align with their values. If the investment is a mutual fund or ETF, you can learn more about how the fund incorporates ESG and how it weights ESG factors by reading its disclosure documents.
- Lower fees: Many ESG ETFs have lower fees, making them a cost-effective option for investors who want to integrate ESG principles into their portfolios. These funds often have lower fees, making them a cost-effective option for investors who want to integrate ESG principles into their portfolios.
Examples of ESG funds and ETFs:
- ESGV (ESG U.S. Stock ETF): Indexed (approx. 1,500 stocks)
- VFTAX (FTSE Social Index Fund): Indexed (approx. 500 stocks)
- VSGX (ESG International Stock ETF): Indexed (approx. 3,000-4,000 stocks)
- VEIGX (Global ESG Select Stock Fund): Actively managed (approx. 40-50 stocks)

Q: What role do ESG stocks and responsible investing play in creating sustainable portfolios?
A: ESG stocks, which are shares of companies with strong ESG performance, are essential components of responsible investing strategies. Responsible investing involves integrating ESG factors into investment decisions to create portfolios that align with ethical values and promote sustainability. ESG investing is a form of sustainable investing that considers environmental, social and governance factors to judge an investment’s financial returns and its
- Positive screening: Investors can select companies with positive ESG attributes, such as low carbon emissions, strong labor practices, and ethical governance. Gender-focused ESG funds select companies with significant female leadership while green funds might focus on companies that limit water consumption or carbon emissions.
- Negative screening: Investors can exclude companies involved in activities that conflict with their values, such as fossil fuels, tobacco, or weapons manufacturing.
- Engagement: Investors can engage with companies to encourage them to improve their ESG performance.
By incorporating ESG stocks into their portfolios and practicing responsible investing, investors can create sustainable portfolios that generate financial returns while contributing to a more sustainable and equitable world.
Q: How can investors avoid greenwashing and ensure the integrity of their ESG investments?
A: Greenwashing, the practice of falsely portraying a company or product as environmentally friendly, is a significant concern in ESG investing. To avoid greenwashing and ensure the integrity of their ESG investments, investors should:
- Rely on reputable ESG scores and ratings: Utilize ESG ratings from established providers such as Morgan Stanley Institute for Sustainable Investing and Morningstar to assess companies’ ESG performance.
- Conduct thorough due diligence: Investigate companies’ ESG practices and verify their claims through independent sources.
- Read disclosure documents carefully: Review fund prospectuses and ESG reports to understand how ESG factors are integrated into the investment process.
- Engage with companies: Ask companies questions about their ESG performance and hold them accountable for their commitments.
- Understand ESG investment risk: Be aware of the chance that the stocks or bonds screened by the index provider or advisor, as applicable, for ESG criteria generally will underperform the market as a whole or, in the aggregate, will trail returns of other funds screened for ESG criteria.

The Future Landscape of Sustainable Finance and ESG
The momentum behind ESG investing is not just a passing trend but a fundamental shift in how investors view financial returns and societal impact. As awareness of environmental and social issues continues to grow and regulatory pressures intensify, ESG investing is poised to become even more mainstream in the years to come. The sustainable finance growth will likely accelerate, driven by increasing demand for ESG funds, ESG ETFs, and other sustainable investment products. Companies that prioritize ESG principles will be better positioned to attract capital, enhance their brand reputation, and create long-term value for stakeholders.

Conclusion: Embracing ESG Investing for a Sustainable Future
ESG investing is rapidly becoming a huge deal in sustainable finance because it aligns financial returns with positive environmental and social outcomes. By considering environmental, social, and governance factors alongside financial metrics, investors can make informed decisions that contribute to a more sustainable and equitable world. As the sustainable finance growth continues, ESG investing will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of finance and driving positive change. Embracing ESG principles is not just a responsible investment strategy but also a pathway to creating a more sustainable and prosperous future for all.
Before diving into FAQs, remember that ESGPro Mastery Institute (https://esgproinvest.com/) can help you bridge the gap between sustainability theory and investment-grade performance. Explore our ESG reporting and sustainability training services today!
FAQs About ESG Investing and Sustainable Finance
What are the top trends in sustainable finance for 2025?
The top trends in sustainable finance for 2025 include green bonds, ESG integration, natural disaster response, R&D, carbon pricing and impact investing.
How do ESG factors impact business growth?
ESG practices help reduce businesses’ carbon footprint, making them more sustainable and appealing to environmentally conscious consumers, which ultimately drives business growth. A fact that CFOs, Heads of Sustainability, and decision-makers must recognise. Sustainability reporting standards help drive long-term value.
What is the difference between socially responsible investing (SRI) and ESG investing?
Socially responsible investing (SRI) is often used synonymously with impact investing or sustainable investing and ESG investing is a way of investing in companies based on their commitment to one or more ESG factors.
Why is ESG investing important for institutional investors?
ESG investors help inform the investment choices of large institutional investors such as public pension funds, driving sustainable practices on a larger scale.
What are the main challenges in ESG investing?
The main challenges in ESG investing include greenwashing and accurately measuring impact, requiring investors to conduct thorough due diligence and rely on reputable ESG scores.